Apply SciPy's correlate() to the waveforms of antenna pairs to determine incoming signal directions. More...
Functions | |
| pl.DataFrame | supply_azimuthal_angle_masks (pl.DataFrame skymaps) |
| Supplies azimuth masks to any sky map (eg time delay maps or correlation maps) | |
| pl.DataFrame | combine_time_delay_maps_and_waveforms (pl.DataFrame masks_and_skymaps, pl.DataFrame waveforms) |
| Prepares a big table that has all the column needed by cross_correlate. | |
| pl.DataFrame | cross_correlate (pl.DataFrame big_frame) |
| Compute the zero-centered normalized cross correlation (ZNCC) and makes correlation skymaps. | |
| [float, float] | _get_true_direction (ROOT.pueo.Dataset dataset) |
| Returns the true signal direction. | |
| None | plot_correlation_map (pl.DataFrame correlation_frame, str plot_name, true_phi=None, true_theta=None) |
| Plots the reult of cross_correlate. | |
Detailed Description
Apply SciPy's correlate() to the waveforms of antenna pairs to determine incoming signal directions.
Function Documentation
◆ supply_azimuthal_angle_masks()
| pl.DataFrame supply_azimuthal_angle_masks | ( | pl.DataFrame | skymaps | ) |
Supplies azimuth masks to any sky map (eg time delay maps or correlation maps)
- Parameters
-
[in] skymaps columns A1_PhiSectorandA2_PhiSectorare required
- Return values
-
phi_masks see the schema of the example output below
- Parameters:
- Input: required columns are the \(\phi\)-sectors of the antenna pairs,
A1_PhiSectorandA2_PhiSector. - Output schema: one column (
masks) will be attached to the input dataframe,$ A1_PhiSector <u8>$ A2_PhiSector <u8>$ masks <array[bool, (1, 360)]>
- Input: required columns are the \(\phi\)-sectors of the antenna pairs,
- Explanation:
- \(\phi\)-sector 1 is centered around 0 degrees azimuth, \(\phi\)-sector 2 around 15 degrees, and so on and so forth; the last \(\phi\) sector (24) is centered around 345 degrees.
- Based on the antenna's field of view, the values outside a certain range are dropped.
- In the figure below, we show what this would look like for antennas from the first three and the last \(\phi\)-sectors (white means masked).
- The chosen masking behavior for now is that only the data within the overlapping unmasked range would be kept.
- For instance, suppose an antenna from \(\phi\)-sector 1 is paired with an antenna from \(\phi\)-sector 2, then:
- Warning
- Thus, if the antenna pair's fields of view do not overlap, then everything will be masked.
Definition at line 34 of file locate_signal.py.
◆ combine_time_delay_maps_and_waveforms()
| pl.DataFrame combine_time_delay_maps_and_waveforms | ( | pl.DataFrame | masks_and_skymaps, |
| pl.DataFrame | waveforms ) |
Prepares a big table that has all the column needed by cross_correlate.
- Parameters
-
[in] masks_and_skymaps The output of supply_azimuthal_angle_masks [in] waveforms The output of waveform_plots.load_waveforms
- Return values
-
big_frame See sample output schema below.
- Parameters:
- The following columns are required in
waveforms:AntNumwaveforms (volts)step size (nanoseconds)Pol
- The following columns are required in
masks_and_skymaps:A1_AntNumA2_AntNumtime delays [sec]masks
- The output schema: $ A1_AntNum <enum>$ A2_AntNum <enum>$ Pol <enum>$ A1_waveforms (volts) <array[f64, 3072]>$ A2_waveforms (volts) <array[f64, 3072]>$ time delays [samples] <array[i64, (180, 360)]>$ masks <array[bool, (1, 360)]>
- The following columns are required in
- Explanation:
time delays [samples]refers to the time delay skymaps, with the units converted from seconds to "samples"- That is, the units are in "steps" (
step size (nanoseconds)) - The values in these time delay skymaps are therefore integers, serving as indices.
- These indices are then used later in cross_correlate when creating the correlation skymaps based on the time delay maps (via "fancy-indexing").
- Qualitatively, the time delay maps have not changed. For example: Time Delay Map in SecondsTime Delay Map in Samples
Definition at line 149 of file locate_signal.py.
◆ cross_correlate()
| pl.DataFrame cross_correlate | ( | pl.DataFrame | big_frame | ) |
Compute the zero-centered normalized cross correlation (ZNCC) and makes correlation skymaps.
- Parameters
-
[in] big_frame The output of combine_time_delay_maps_and_waveforms()
- Return values
-
correlation_maps See the schema of the example output below
Parameters: columns
correlationandcorrelation mapswill be added to the input, so the output schema looks like$ A1_AntNum <enum>$ A2_AntNum <enum>$ Pol <enum>$ A1_waveforms (volts) <array[f64, 3072]>$ A2_waveforms (volts) <array[f64, 3072]>$ time delays [samples] <array[i64, (180, 360)]>$ masks <array[bool, (1, 360)]>$ correlation <array[f64, 6143]>$ correlation maps <array[f64, (180, 360)]>correlation mapscontain correlation skymaps. These are matrices with the same dimensions as the time delay maps oftime delays [samples], as the former are made based on the latter via "fancy-indexing"- Each matrix element of a correlation skymap is the correlation score between two waveforms, given some particular time delay, ie. phase shift.
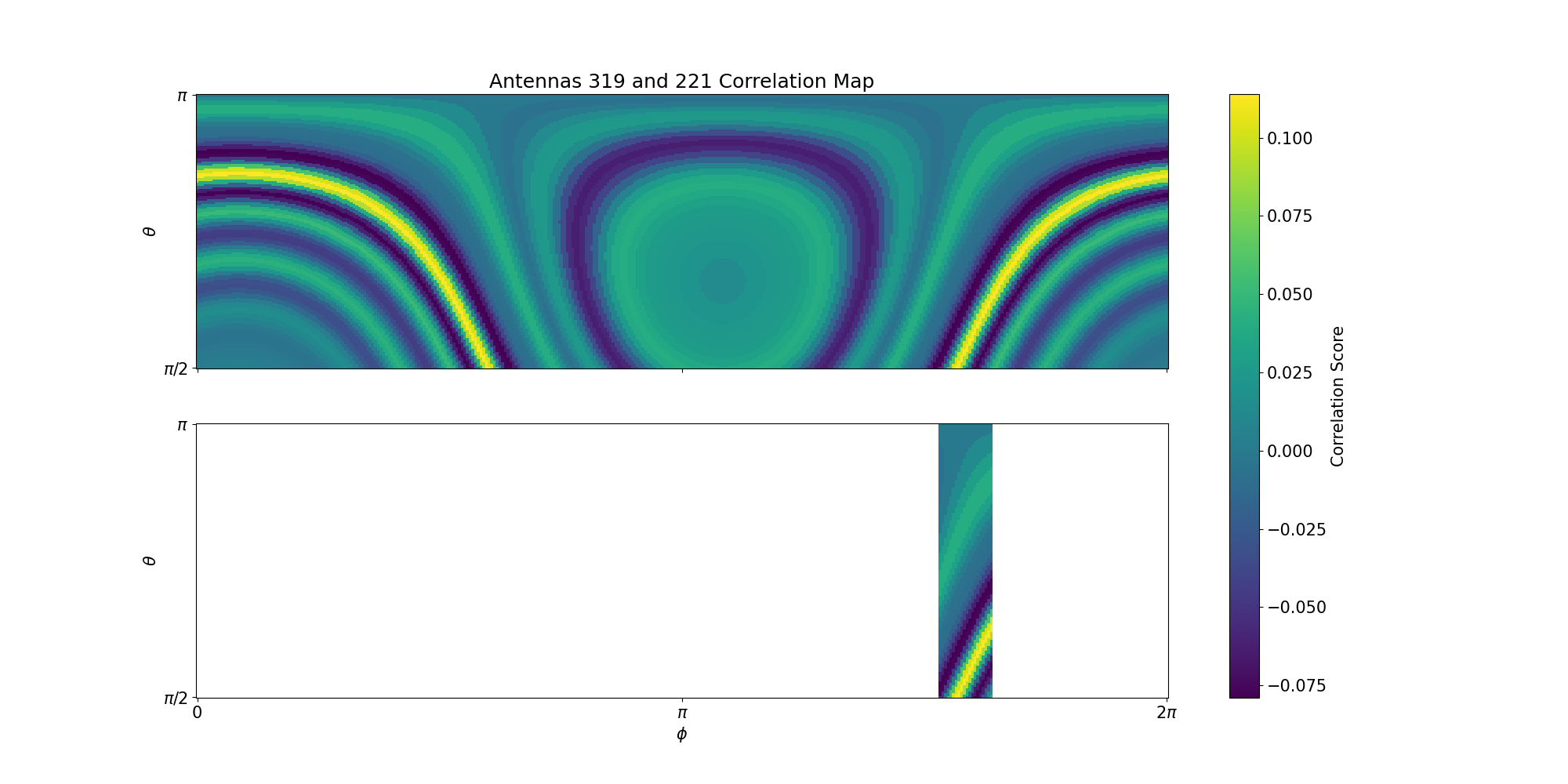
maskscan be used to mask the correlation maps, as shown in the bottom subplot in the Figure above. The masks are defined by supply_azimuthal_angle_masks.
- Explanation:
- Consider two waveforms,
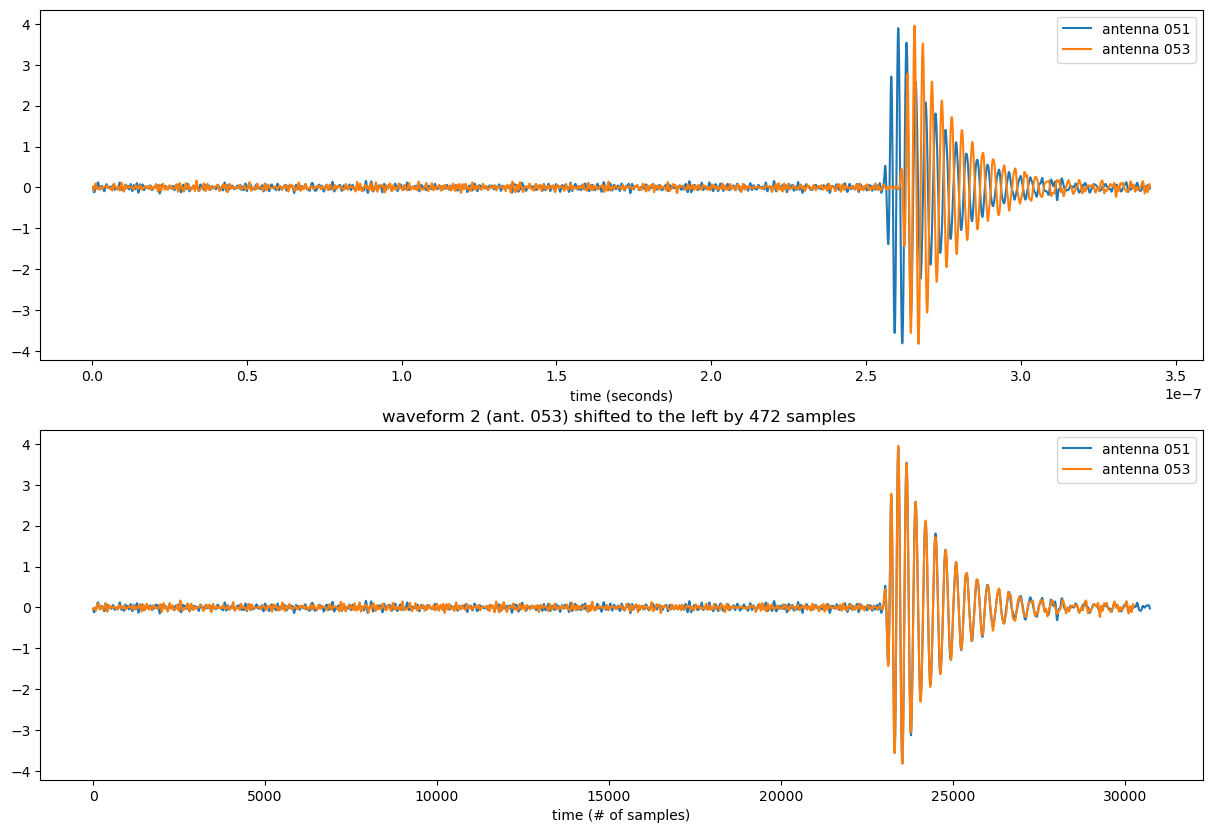
- Each row in the
correlationcolumn is an array of correlation scores. - By shifting the waveforms we may be able to get them to align perfectly, at which point maximum correlation is achieved.
- The correlation score tells us how "aligned" the two waveforms are after we phase shift
A1_waveforms (volts)againstA2_waveforms (volts)by a certain amount of time. - The waveforms are zero-centered and normalized such that the cross-correlation is bounded between [-1,1]. Zero means the waveforms are not aligned at all.
- See cross_correlation_and_time_delay.pdf or, for details, scipy_correlate_behavior.pdf.
- Consider two waveforms,
Definition at line 217 of file locate_signal.py.
◆ _get_true_direction()
|
protected |
Returns the true signal direction.
- Parameters
-
[in] dataset The output of initialise.load_pueoEvent_Dataset
- Note that as stored in the
.rootfiles, the variableRFdir_payloadis the direction the signal is travelling to. - Therefore, to obtain the direction that the signal is coming from, we need the opposite vector.
- Thus, \(\phi_{\rm true} = (\phi_{\rm rfdir} + 180 ^\circ) \% 360^\circ\), and \(\theta_{\rm true} = 180^\circ - \theta_{\rm rfdir}\)
Definition at line 299 of file locate_signal.py.
◆ plot_correlation_map()
| None plot_correlation_map | ( | pl.DataFrame | correlation_frame, |
| str | plot_name, | ||
| true_phi = None, | |||
| true_theta = None ) |
Plots the reult of cross_correlate.
- Parameters
-
[in] correlation_frame The output of cross_correlate [in] plot_name Remember to specify file type [in] true_phi (optional) from _get_true_direction [in] true_theta (optional) from _get_true_direction
- Required columns in
correlation_frame:correlation mapsmasksPol
- Using only one antenna pair, one can find a band of peak correlation scores, see the plot in the file description.
- If we then sum over all antenna pairs, we would be able to identify a single peak:
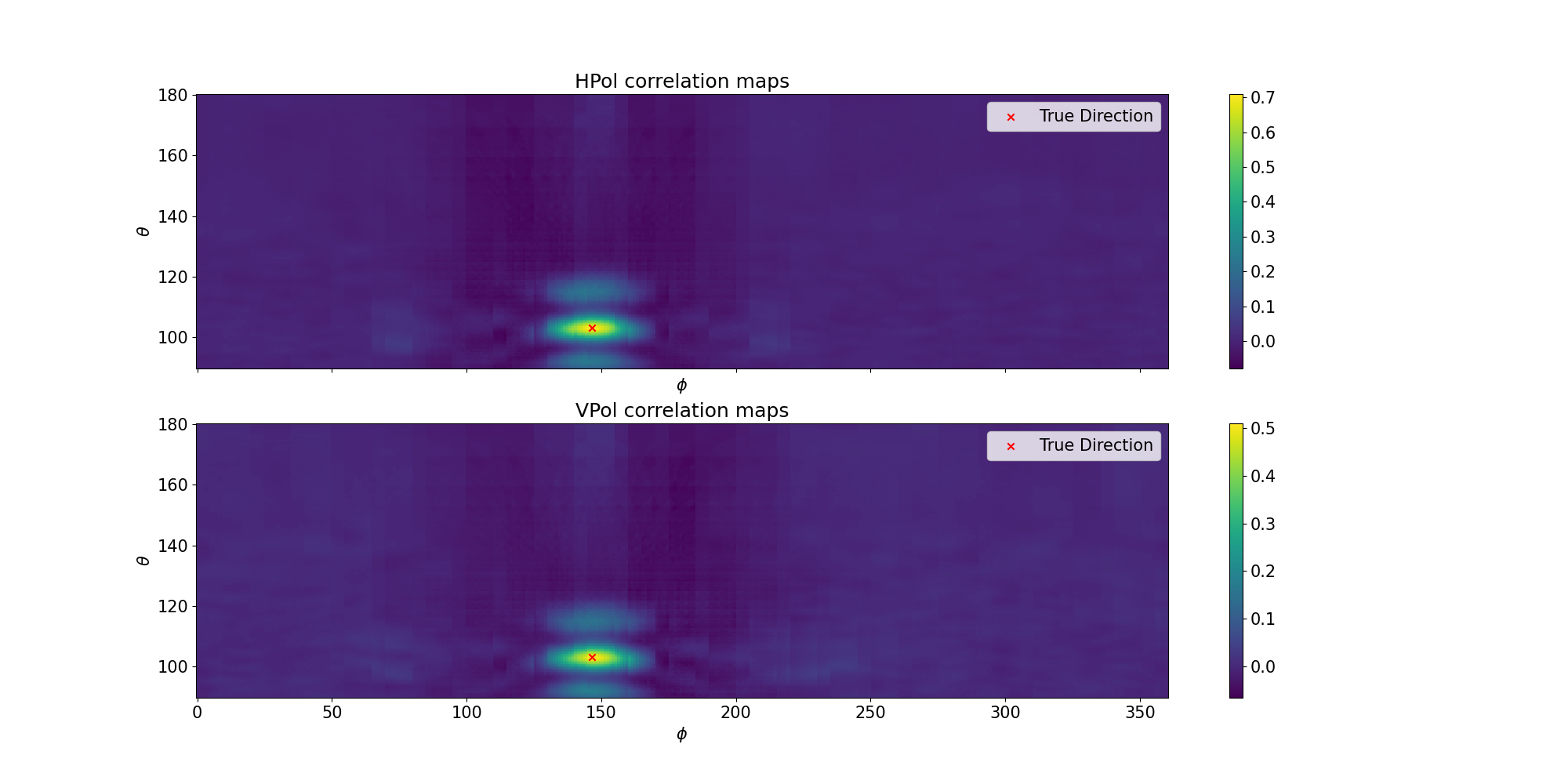
Definition at line 319 of file locate_signal.py.