3@brief `main()` shows how to use [cross_correlate()](#locate_signal.cross_correlate)
4and [plot_correlation_map()](#locate_signal.plot_correlation_map).
6\anchor example_one_pair_corr_map
7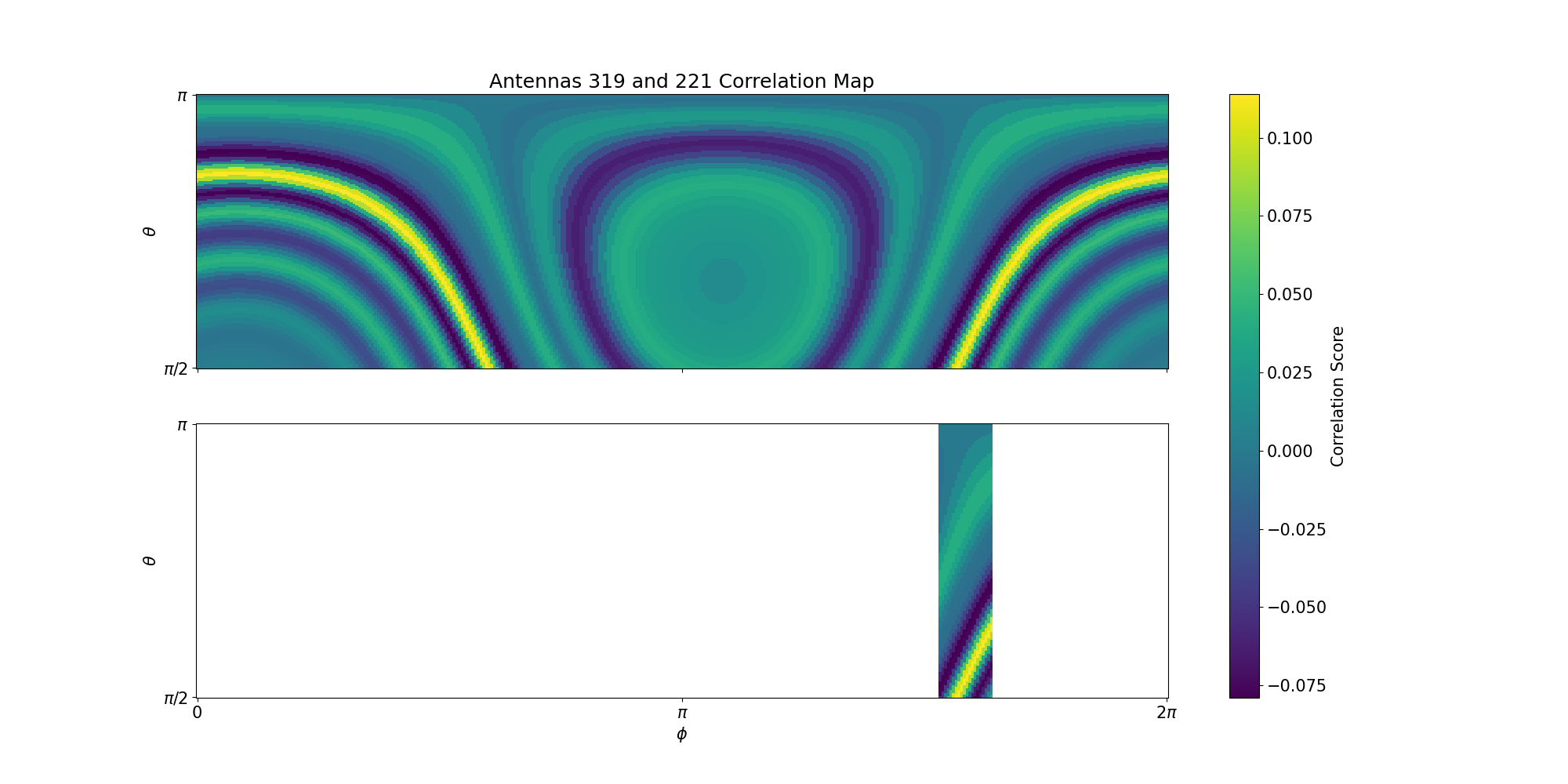
9Summing over all antenna pairs, we have
11\anchor example_corr_map
12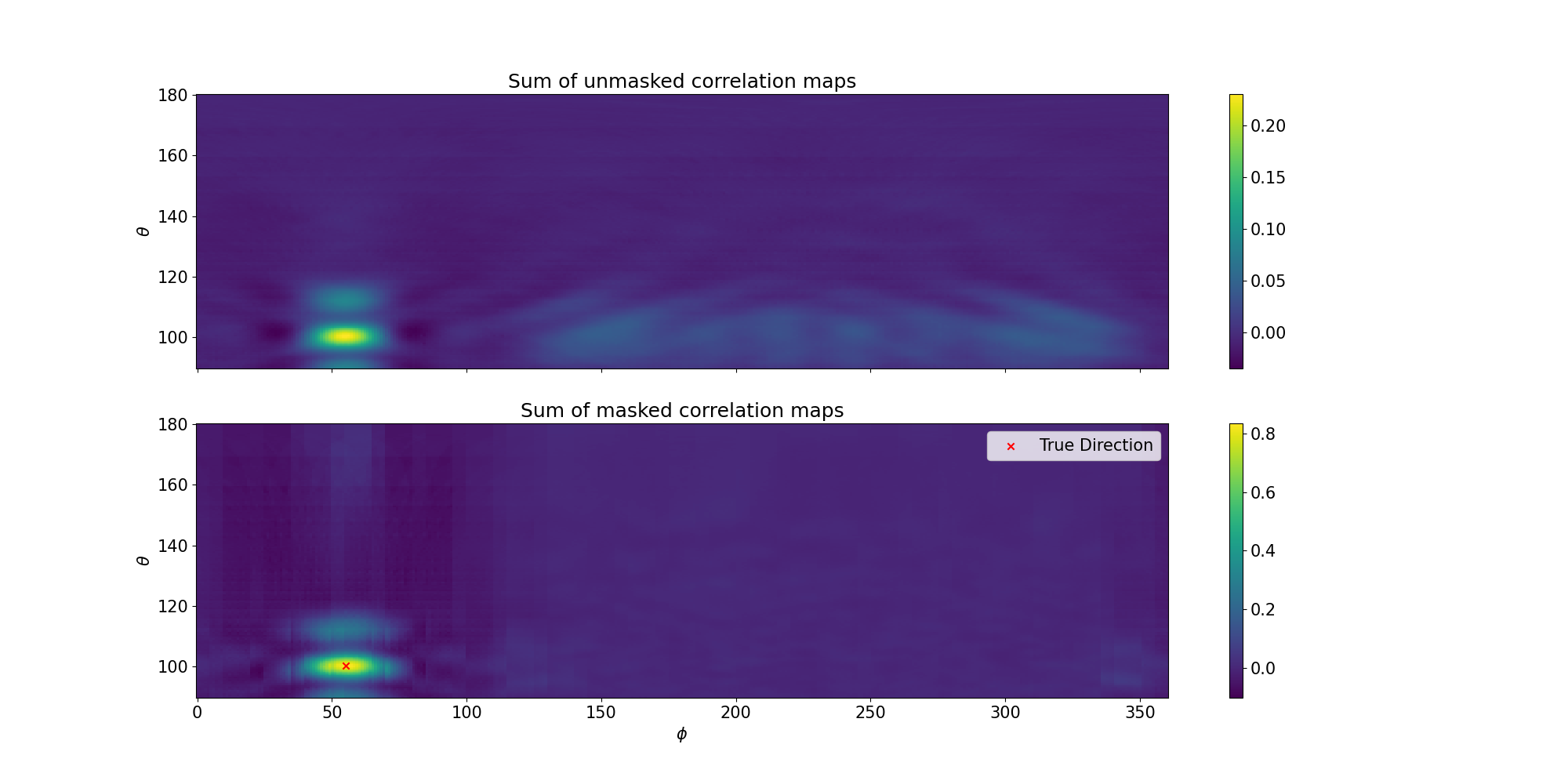
14We can see that by masking the individual correlation maps, the total correlation map is less
22from time_delays
import _make_grid
23from pathlib
import Path
24from initialise
import load_pueoEvent_Dataset
34def supply_azimuthal_angle_masks(skymaps: pl.DataFrame) -> pl.DataFrame:
35 r"""!Supplies azimuth masks to any sky map
36 (eg [time delay maps](#time_delays.make_time_delay_skymap) or
37 [correlation maps](#cross_correlate))
39 @param[in] skymaps columns `A1_PhiSector` and `A2_PhiSector` are **required**
40 @retval phi_masks see the schema of the example output below
43 * Input: required columns are the \f$\phi\f$-sectors of the antenna pairs,
44 `A1_PhiSector` and `A2_PhiSector`.
45 * Output schema: one column (`masks`) will be attached to the input dataframe,
49$ masks <array[bool, (1, 360)]>
54 * \f$\phi\f$-sector 1 is centered around 0 degrees azimuth, \f$\phi\f$-sector 2 around 15 degrees,
55 and so on and so forth; the last \f$\phi\f$ sector (24) is centered around 345 degrees.
56 * Based on the antenna's [field of view](#antenna_attributes.ASSUMED_PHI_SECTOR_APERTURE_WIDTH),
57 the values outside a certain range are dropped.
58 * In the figure below, we show what this would look like for antennas from the first three and
59 the last \f$\phi\f$-sectors (white means masked).
61 
63 * The chosen masking behavior for now is that **only the data within the overlapping unmasked
64 range would be kept**.
65 * For instance, suppose an antenna from \f$\phi\f$-sector 1 is paired with an antenna from
66 \f$\phi\f$-sector 2, then:
68 
71 * Thus, if the antenna pair's
72 [fields of view](#antenna_attributes.ASSUMED_PHI_SECTOR_APERTURE_WIDTH)
73 do not overlap, then everything will be masked.
75 from antenna_attributes
import NUM_PHI_SECTORS, ASSUMED_PHI_SECTOR_APERTURE_WIDTH
76 phi, _ = _make_grid(sparse=
True)
83 {
"PhiSector": np.arange(1, 25)}, schema={
"PhiSector": pl.UInt8}
87 ((pl.col(
"PhiSector") - 1) * (360 / NUM_PHI_SECTORS)).alias(
"aperture center [deg]")
91 pl.col(
"aperture center [deg]"),
93 (pl.col(
"aperture center [deg]") - ASSUMED_PHI_SECTOR_APERTURE_WIDTH / 2)
94 ).alias(
"left bound [deg]"),
96 (pl.col(
"aperture center [deg]") + ASSUMED_PHI_SECTOR_APERTURE_WIDTH / 2)
97 ).alias(
"right bound [deg]"),
104 aperture_bounds.select(
106 pl.col(
"left bound [deg]").alias(
"A1 left"),
107 pl.col(
"right bound [deg]").alias(
"A1 right"),
108 ), left_on=
"A1_PhiSector", right_on=
"PhiSector"
110 aperture_bounds.select(
112 pl.col(
"left bound [deg]").alias(
"A2 left"),
113 pl.col(
"right bound [deg]").alias(
"A2 right"),
114 ), left_on=
"A2_PhiSector", right_on=
"PhiSector"
116 pl.struct(pl.col(
"A1 left"), pl.col(
"A1 right"))
120 ((phi - left) % 360) < ((right - left) % 360)
125 pl.struct(pl.col(
"A2 left"), pl.col(
"A2 right"))
129 ((phi - left) % 360) < ((right - left) % 360)
137 "A1 masks",
"A2 masks",
"A1 left",
"A2 left",
"A1 right",
"A2 right"
139 pl.struct(
"A1 masks",
"A2 masks").map_batches(
141 ~(m1 & m2)
for m1, m2
in s.to_numpy()
149def combine_time_delay_maps_and_waveforms(masks_and_skymaps: pl.DataFrame,
150 waveforms: pl.DataFrame) -> pl.DataFrame:
151 r"""!Prepares a big table that has all the column needed by #cross_correlate.
153 @param[in] masks_and_skymaps The output of #supply_azimuthal_angle_masks
154 @param[in] waveforms The output of #waveform_plots.load_waveforms
155 @retval big_frame See sample output schema below.
158 * The following columns are required in `waveforms`:
160 -# `waveforms (volts)`
161 -# `step size (nanoseconds)`
163 * The following columns are required in `masks_and_skymaps`:
166 -# `time delays [sec]`
173$ A1_waveforms (volts) <array[f64, 3072]>
174$ A2_waveforms (volts) <array[f64, 3072]>
175$ time delays [samples] <array[i64, (180, 360)]>
176$ masks <array[bool, (1, 360)]>
179 * `time delays [samples]` refers to the [time delay skymaps](#time_delays.make_time_delay_skymap),
180 with the units converted from seconds to "samples"
181 * That is, the units are in "steps" (`step size (nanoseconds)`)
182 * The values in these time delay skymaps are therefore integers, serving as indices.
183 * These indices are then used later in #cross_correlate when creating the
184 correlation skymaps based on the time delay maps (via "fancy-indexing").
185 * Qualitatively, the time delay maps have not changed. For example:
186 \image html time_delay_map_in_seconds.svg Time Delay Map in Seconds width=40%
187 \image html time_delay_map_in_samples.svg Time Delay Map in Samples width=40%
190 signal_length = len(waveforms[
"waveforms (volts)"][0])
191 step_size = waveforms[
"step size (nanoseconds)"][0] * 1e-9
195 .join(waveforms, left_on=
"A1_AntNum", right_on=
"AntNum")
196 .join(waveforms, left_on=[
"A2_AntNum",
"Pol"], right_on=[
"AntNum",
"Pol"])
199 pl.col(
"time delays [sec]") / step_size + signal_length - 1
202 .map_batches(
lambda s: np.rint(s.to_numpy()).astype(int))
203 .alias(
"time delays [samples]")
206 pl.col(
"waveforms (volts)").alias(
"A1_waveforms (volts)"),
207 pl.col(
"waveforms (volts)_right").alias(
"A2_waveforms (volts)")
210 r"^A[12]_AntNum$",
"Pol",
r"^A[12]_waveforms \(volts\)$",
"time delays [samples]",
"masks"
217def cross_correlate(big_frame: pl.DataFrame) -> pl.DataFrame:
218 r"""!Compute the zero-centered normalized cross correlation (ZNCC) and makes correlation skymaps
220 @param[in] big_frame The output of #combine_time_delay_maps_and_waveforms()
221 @retval correlation_maps See the schema of the example output below
223 * Parameters: columns `correlation` and `correlation maps` will be added to the input,
224 so the output schema looks like
229$ A1_waveforms (volts) <array[f64, 3072]>
230$ A2_waveforms (volts) <array[f64, 3072]>
231$ time delays [samples] <array[i64, (180, 360)]>
232$ masks <array[bool, (1, 360)]>
233$ correlation <array[f64, 6143]>
234$ correlation maps <array[f64, (180, 360)]>
236 * `correlation maps` contain correlation skymaps.
237 These are matrices with the same dimensions as the time delay maps of `time delays [samples]`,
238 as the former are made based on the latter via "fancy-indexing"
240 * Each matrix element of a correlation skymap is the correlation score between two waveforms,
241 given some particular [time delay](#time_delays.make_time_delay_skymap), ie. phase shift.
243 
245 * `masks` can be used to mask the correlation maps, as shown in the bottom subplot in the
246 Figure above. The masks are defined by #supply_azimuthal_angle_masks.
248 \anchor scipy_corr_expl
250 * Consider two waveforms,
251 \anchor maxcorrachieved
252 \image html shift_by_472_samples.png
253 * Each row in the `correlation` column is an array of correlation scores.
254 * By shifting the waveforms we may be able to get them to align perfectly,
255 at which point maximum correlation is achieved.
256 * The correlation score tells us how "aligned" the two waveforms are after we phase shift
257 `A1_waveforms (volts)` against `A2_waveforms (volts)` by a certain amount of time.
258 * The waveforms are zero-centered and normalized such that the cross-correlation is
259 bounded between [-1,1]. Zero means the waveforms are not aligned at all.
260 * See [cross_correlation_and_time_delay.pdf](cross_correlation_and_time_delay.pdf) or,
261 for details, [scipy_correlate_behavior.pdf](scipy_correlate_behavior.pdf).
264 from scipy.signal
import correlate
266 correlation_maps: pl.DataFrame = (
270 pl.struct(
"A1_waveforms (volts)",
"A2_waveforms (volts)")
275 (wf1 - np.mean(wf1)) / np.std(wf1),
276 (wf2 - np.mean(wf2)) / np.std(wf2),
279 for wf1, wf2
in s.to_numpy()
282 .alias(
"correlation"),
286 pl.struct(pl.col(
"time delays [samples]"), pl.col(
"correlation")).map_batches(
288 [correlation_array[time_delay_matrix]
289 for time_delay_matrix, correlation_array
292 ).alias(
"correlation maps")
296 return correlation_maps
299def _get_true_direction(dataset: ROOT.pueo.Dataset) -> [float, float]:
301 @brief Returns the true signal direction
303 @param[in] dataset The output of #initialise.load_pueoEvent_Dataset
305 * Note that as stored in the `.root` files,
306 the variable `RFdir_payload` is the direction the signal is travelling **to**.
307 * Therefore, to obtain the direction that the signal is coming **from**,
308 we need the opposite vector.
309 * Thus, \f$\phi_{\rm true} = (\phi_{\rm rfdir} + 180 ^\circ) \% 360^\circ\f$,
310 and \f$\theta_{\rm true} = 180^\circ - \theta_{\rm rfdir}\f$
313 truePhi = (dataset.truth().payloadPhi + 180) % 360
314 trueTheta = 180 - dataset.truth().payloadTheta
316 return truePhi, trueTheta
319def plot_correlation_map(correlation_frame: pl.DataFrame, plot_name: str,
320 true_phi=
None, true_theta=
None) ->
None:
322 @brief Plots the reult of #cross_correlate.
324 @param[in] correlation_frame The output of #cross_correlate
325 @param[in] plot_name Remember to specify file type
326 @param[in] true_phi (optional) from #_get_true_direction
327 @param[in] true_theta (optional) from #_get_true_direction
329 * Required columns in `correlation_frame`:
330 -# `correlation maps`
334 * Using only one antenna pair, one can find a band of peak correlation scores,
335 see the [plot in the file description](@ref example_one_pair_corr_map).
337 * If we then sum over all antenna pairs, we would be able to identify a single peak:
339 
342 import matplotlib.pyplot
as plt
343 import numpy.ma
as ma
344 plt.rcParams.update({
'font.size': 15})
346 phi, theta = _make_grid(sparse=
True)
347 phi = np.degrees(phi)
348 theta = np.degrees(theta)
350 fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 1, figsize=(20, 10), sharex=
True)
351 for i, df
in enumerate(correlation_frame.partition_by(
"Pol")):
352 corr_map = df[
"correlation maps"].to_numpy()
355 masks = np.repeat(df[
"masks"].to_numpy(), repeats=np.shape(corr_map)[1], axis=1)
356 masks_sum = np.sum(~masks, axis=0)
358 corr_map_masked = ma.array(corr_map, mask=masks)
361 total_masked = np.sum(corr_map_masked, axis=0) / masks_sum
363 axes[i].set_ylabel(
r"$\theta$")
364 axes[i].set_xlabel(
r"$\phi$")
365 axes[i].set_title(f
"{df["Pol
"][0]}Pol correlation maps")
366 fig.colorbar(axes[i].pcolormesh(phi, theta, total_masked))
368 if true_phi
is not None and true_theta
is not None:
369 axes[i].scatter(true_phi, true_theta, marker=
'x', color=
"red", label=
'True Direction')
372 fig.savefig(plot_name)
376def __plot_example_correlation_map_for_one_antenna_pair(input_frame: pl.DataFrame):
377 import matplotlib.pyplot
as plt
378 import numpy.ma
as ma
379 plt.rcParams.update({
'font.size': 15})
381 pl.Config().set_tbl_cols(input_frame.width)
382 pl.Config().set_fmt_table_cell_list_len(0)
386 mask = input_frame[
"masks"].to_numpy().squeeze()
387 corr_map = input_frame[
"correlation maps"].to_numpy().squeeze()
390 mask = np.vstack([mask] * corr_map.shape[0])
391 corr_map_masked = ma.array(corr_map, mask=mask)
394 phi, theta = _make_grid(sparse=
True)
396 fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 1, sharex=
True, figsize=(20, 10))
398 f
"Antennas {input_frame["A1_AntNum
"][0]} and {input_frame["A2_AntNum
"][0]} Correlation Map"
401 ax.set_ylabel(
r"$\theta$")
402 ax.set_yticks([np.pi / 2, np.pi], labels=[
r"$\pi / 2$",
r"$\pi$"])
404 axes[1].set_xlabel(
r"$\phi$")
405 axes[1].set_xticks([0, np.pi, 2 * np.pi], labels=[
"0",
r"$\pi$",
r"$2\pi$"])
406 image = axes[0].pcolormesh(phi, theta, corr_map, vmin=corr_map.min(), vmax=corr_map.max())
407 image = axes[1].pcolormesh(phi, theta, corr_map_masked, vmin=corr_map.min(), vmax=corr_map.max())
408 fig.colorbar(image, ax=axes.ravel().tolist(), label=
"Correlation Score")
409 plt.savefig(
"img/example_correlation_map_one_pair.png")
412if __name__ ==
"__main__":
414 from antenna_attributes
import read_MI_antenna_geometry, get_MI_nominal_phase_center
415 from antenna_pairs
import generate_MI_antenna_pairs
416 from time_delays
import make_time_delay_skymap
417 from waveform_plots
import load_waveforms, upsample_waveforms
421 _jun25: Path = os.environ.get(
"PUEO_UTIL_INSTALL_DIR") / Path(
"share/pueo/geometry/jun25/qrh.dat")
422 _face_centers: pl.DataFrame = read_MI_antenna_geometry(qrh_dot_dat=_jun25)
424 _phase_centers: pl.DataFrame = (
425 get_MI_nominal_phase_center(face_centers=_face_centers)
426 .select(
"AntNum",
"PhiSector",
"AntIdx",
"X[m]",
"Y[m]",
"Z[m]")
431 _antenna_pairs: pl.DataFrame = generate_MI_antenna_pairs(antennas=_phase_centers)
432 _time_delays: pl.DataFrame = (
433 make_time_delay_skymap(antenna_pairs=_antenna_pairs)
434 .select(pl.col(
r"^A[12]_AntNum$",
r"^A[12]_PhiSector$",
"time delays [sec]"))
439 masked: pl.DataFrame = (
440 supply_azimuthal_angle_masks(skymaps=_time_delays)
441 .select(pl.col(
r"^A[12]_AntNum$",
"time delays [sec]",
"masks"))
446 _run_zero_data: ROOT.pueo.Dataset = load_pueoEvent_Dataset(pueo_mc_data=Path(
"/tmp"), run_number=0)
447 _run_zero_data.last()
449 _wf: pl.DataFrame = (
450 load_waveforms(dataset=_run_zero_data)
451 .select(
"AntNum",
"Pol",
"waveforms (volts)",
"step size (nanoseconds)")
453 up: pl.DataFrame = upsample_waveforms(waveforms=_wf, upsample_factor=3)
457 big_frame = combine_time_delay_maps_and_waveforms(masks_and_skymaps=masked, waveforms=up)
459 correlation_frame: pl.DataFrame = cross_correlate(big_frame)
463 tp, tt = _get_true_direction(dataset=_run_zero_data)
464 plot_correlation_map(
465 correlation_frame=correlation_frame, true_phi=tp, true_theta=tt,
466 plot_name=
'img/example_correlation_map_two_pols.png'